Our Services
Main business being Agro-forestry products such as cashew, gum Arabic, Timber, charcoal, cocoa beans, Honey, stone flower, hibiscus flowers, also farm products like dehydrated ginger, garlic, green leafy vegetables, jaggery and jaggery products.
Gum Arabic
Gum arabic, also known as acacia gum, is a natural substance derived from the sap of Acacia trees, primarily Acacia senegal and Acacia seyal. It has been used for centuries in various applications due to its unique properties. Here are some key points about Gum Arabic
Timber
Timber refers to wood that has been processed or cut for use in construction, furniture making, paper production, and other applications. It is obtained from trees through logging and subsequent processing. Here are some key points about timber

Charcoal
Charcoal is a lightweight black carbon residue produced by removing water and other volatile constituents from animal and vegetation substances through the process of slow pyrolysis, which occurs in the absence of oxygen. Here are some key points about charcoal
Honey
Honey is a natural sweet substance produced by honey bees from the nectar of flowers. It has been consumed by humans for thousands of years and is valued not only for its sweetness but also for its various health benefits and culinary uses. Here are some key points about honey
Stone Flower
Stone flower, also known as “Dagad phool” or “Parmotrema perlatum,” is a unique spice commonly used in Indian cuisine, particularly in dishes from the Maharashtra region. Here are some key points about stone flower

Hibiscus Flowers
Hibiscus flowers, belonging to the genus Hibiscus, are vibrant and colorful blooms known for their beauty and versatility. Here are some key points about hibiscus flowers

Ginger
Ginger is a popular spice that is widely used in cooking and traditional medicine. It is derived from the rhizome of the ginger plant (Zingiber officinale) and has a pungent, spicy flavor with hints of sweetness. Here are some key points about ginger
Garlic
Garlic, scientifically known as Allium sativum, is a species in the onion genus, Allium. It is widely cultivated for its distinctive flavor and aroma, as well as its culinary and medicinal properties. Here are some key points about garlic

Green Leafy Vegetables
Green leafy vegetables are an essential part of a healthy diet, providing a rich array of vitamins, minerals, fiber, and phytonutrients. They come in various shapes, sizes, and flavors and are prized for their nutritional density and culinary versatility. Here are some examples of common green leafy vegetables

Ginger
Ginger is a popular spice that is widely used in cooking and traditional medicine. It is derived from the rhizome of the ginger plant (Zingiber officinale) and has a pungent, spicy flavor with hints of sweetness. Here are some key points about ginger

Garlic
Garlic, scientifically known as Allium sativum, is a species in the onion genus, Allium. It is widely cultivated for its distinctive flavor and aroma, as well as its culinary and medicinal properties. Here are some key points about garlic

Green Leafy Vegetables
Green leafy vegetables are an essential part of a healthy diet, providing a rich array of vitamins, minerals, fiber, and phytonutrients. They come in various shapes, sizes, and flavors and are prized for their nutritional density and culinary versatility. Here are some examples of common green leafy vegetables
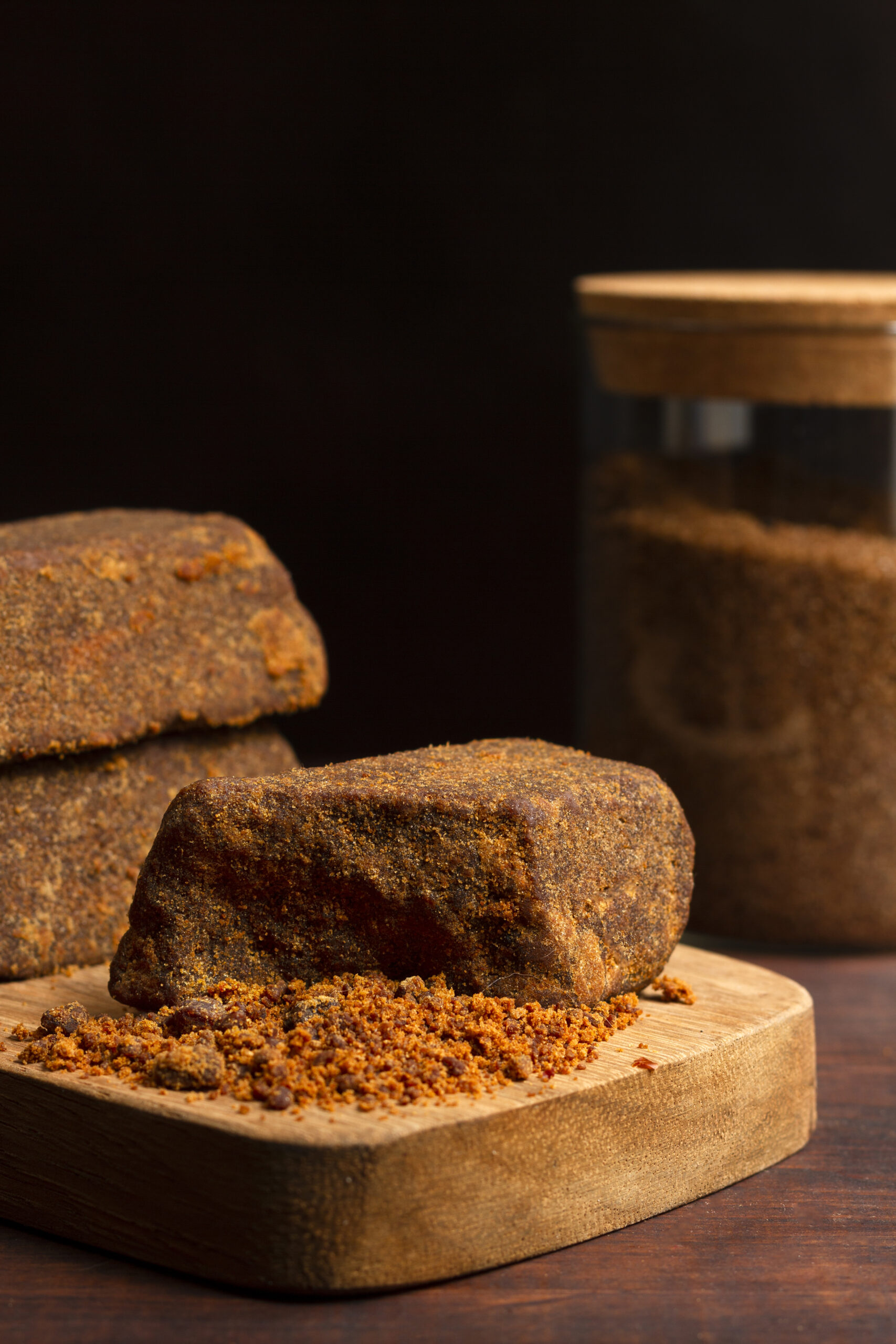
Jaggery Products
Jaggery is a traditional sweetener commonly used in various cuisines around the world, particularly in South Asia. It is made from the concentrated sap or juice of sugarcane or palm trees, which is boiled and then left to cool and solidify. Here are some key points about jaggery and jaggery products:
Supporting Local Farmers & Sustainable Agriculture since 1945
Market Sponsors









